Final report for FW19-347
Project Information
Potato production is a dominant sector of agriculture in northwestern Washington. In Skagit County potatoes are grown on 12,000 acres and the average yield is 20-25 tons/acre. Since potatoes have a high impact on soil nutrition and organic matter, soil quality has become an important priority for potatoes farmers in this area. Arable land is limited in northwestern Washington and land sharing is a common practice in Skagit County. However, it is often difficult for potato farmers to find viable rotation crops based on the extensive amount of acreage they occupy.
Harmony Fields, LLC is an expanding sheep creamery and organic herb farm based in Bow, WA. Fifty percent of this operation’s land is rented from a neighboring potato farm. Harmony Fields is interested in increasing pasture access for their animals over time and require more land each year. It had been well documented that livestock rotations in crop production systems can have positive effects on the soil across farm scale and production type. Also, compost and manure additions can have varying effects on potato quality and disease. More information is needed to better understand the impact of small ruminant grazing rotations in potato production systems.
This project would investigate the consequence of integrating sheep grazing in a potato rotation system by investigating how pasture and sheep manure inputs affect soil-borne tuber disease incidence and severity and soil organic matter quality and nutrition. The project would also document how larger, more established farms can engage with smaller, first generation farms in a relationship that is mutually beneficial.
OBJECTIVES
- Investigate the influence of sheep grazing on potato and soil quality.
- Determine optimal pasture species diversity and access for dairy sheep health in northwestern WA.
- Distribute information to regional and national producers.
Cooperators
- - Producer (Educator and Researcher)
- - Technical Advisor - Producer (Researcher)
Research
Potato Health
Potato Field Trial
In 2019, potato plots were established at Harmony Fields. Plots were established in an area that has been grazed by dairy sheep for the past 8 years (2011-present). Potato plots were established (3 varieties, 3 reps) in May 2019 and managed following organic potato management strategies as per potato growers protocol. Varieties were procured from Bedlington Farms (Lynden, WA0 included 'Chieftan,' 'Yukon Gold' and 'Banana Fingerling.' In-row plots were 10-ft long and set up in a randomized complete block design. This trial was repeated in another area of the same field in 2020 using the same varieties from the same source.
In fall (October 2019/September 2020) potatoes were harvested and examined for size, yield (lbs.), and soil borne disease incidence and severity.
In September 2019, samples of potatoes ('Chieftans'-3 plants per section) from Wallace Farm commercial potato field were sampled and inspected for disease and size. Samples were taken from two areas i) previously grazed by sheep (2 years) and ii) never grazed (corn, barley, orchard grass rotation primarily).
Field trial I was planted May 28th 2019 and harvested October 10th 2019. Field Trial II was planted May 28, 2020 and harvested September 28, 2020. Varieties planted: Chieftan, Yukon Gold, Banana Fingerling
Greenhouse Microplot Experiments
Supplemental greenhouse studies, using soil from sheep pastures from Wallace Farms and relevant potato varieties (see above) were set-up in May 2019. Potatoes were grown in modified buckets (5 gallon) using the collected field soil. Moisture was kept at field capacity using a micro-sprinkler system. Potatoes were assessed at the end of the season (Oct 2019) for disease incidence and severity and size/yield as mentioned above. The experiment was set up as a randomized complete block design (3 treatments, 3 reps) at Harmony Fields. This was not repeated in 2020.
GH trial was planted June 27th 2019 and harvest October 30th 2019. Varieties planting: Chieftan, Yukon Gold, Banana Fingerling
Soil Health
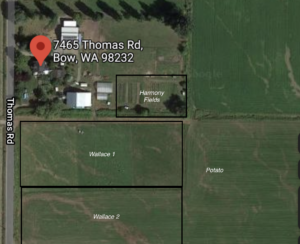
Soil quality parameters (Cornell Assessment of Soil Health) was recorded before planting at Harmony Fields in 2019 and in two areas of rented property adjacent to the farm. Harmony Fields ground has been grazed by sheep for 8+ years, Wallace 1 has been grazed for 4 years, and Wallace 2 had 2 years of sheep grazing followed by potato, followed by 1 yr of sheep grazing. The parameters examined included available water capacity, soil proteins, active carbon, organic matter, pH, extractable potassium, extractable phosphorous, minor elements, soil respiration, and aggregate stability. Composite soil samples (20 subsamples, mixed) were taken from each field and collected as as random representation of the field. In fall 2020, after 1 year of sheep grazing, Wallace 2 was resampled. Also, a nematode community analysis was done on all three fields as well as the adjacent farmland with no prior sheep grazing . See image below. Composite sample were collected in fall 2020 (Field 1-Wallace 2, Field 2-Wallace, Field 3-Harmony Fields, Field 4-Potato) and analyzed by USDA-ARS Corvallis Nematology Lab.
Pasture Plots
Five varietal mixes of grass and legume pasture species (Table 4a) were tested in small plots (4’ x 4’) at Harmony Fields. They were planted in spring/fall (2019). The experiment was set up in a randomized complete block design (3 reps, 5 treatments). Pasture establishment was verified by > 80% coverage at 6 months post-planting. Fresh plant samples were collected in October 2019 and sent to a regional lab (Bar Diamond; Parma, ID) for nutritional analysis. Spring samples were collected and sent to the same lab in June 2020.
A new pasture mix (HF Sheep) was created based on 2019 data and planted in spring 2020 on adjacent land to the current experiment site/rented pasture (Wallace 2). The new field was divided into two sections and the new mix was planted alongside the standard mix (Western Pasture Mix; Skagit Farmers-Burlington, WA) used to plant the previous field. Samples were collected in fall 2020 and sent to Bar Diamond for nutritional analysis
Spring Pasture Trial plated May 28, 2019 and harvested October 1, 2019. Fall Pasture Trial Planted October 9th, 2019 and harvested June 15, 2020.
Results
Potato Health
In field and greenhouse experiments there was no obvious impact of sheep grazing on tuber quality (Tables 1-3). Soil disease rating data needs further analysis before publication, however overall no scab was detected which was the primary concern of the potato grower leasing land. Additional tuber production issues (2019-water damage; 2020-potential late blight and wire worm) made have impacted yield. The samples taken from the production field did not have any obvious disease and in a 2019 post-harvest check-in with the field manager/co-owner there were no commercial production or quality complaints from tubers grown in an area that previously supported sheep grazing.
Soil Health
CASH: ACE Soil protein, Soil Respiration, and Aggregate Stability (Table 9) were all highest in the field with 8+ years of sheep grazing. Wallace 1 field (4 year of consistent sheep grazing) also measured better than Wallace 2 across several parameters, a field which had recently gone from standard vegetable production to 2 years of sheep grazing to 1 year of organic potato production and then back to sheep grazing in 2020.
Nematode Community: The Harmony Fields soil (Field 3) had the most diversity of beneficial nematodes and more bacterial feeding nematodes overall than the other soils (Table 10). Soils with some history of sheep grazing overall had a more diverse community of beneficial nematodes as compared to the adjacent field soil with no prior history of small ruminant presence (Field 4). Field 4 has a history of organic potato, orchard grass, corn, and barley rotations primarily. However, plant parasitic pin nematodes were abundant in Harmony Fields soil as compared to Wallace 1 & Wallace 2.
Pasture Plots
While results showed that pasture species nutritional quality fluctuated seasonally as expected, there were no obvious differences between spring vs. fall planted pasture species (Tables 4 & 5). It is still hard to determine the optimal mix of pasture species, however all of the chosen species were able to establish in this region with adequate cover (80-90 %, data not shown). Legume species provided the most consistent crude protein, however the Timothy also did well, especially in the later months of the grazing season (June-Oct). The new pasture mix that was created in 2020 using these species offered the highest crude protein (Table 8), however other sheep health concerns need to be taken into consideration since it is higher in percent legume species than the standard mix and may lead to bloat in sheep (Puget Sound Vet Group, personal communication).
Conclusions
It is meaningful to note that sheep grazing did not negatively impact tuber quality based on this research and this information has supported continual land sharing opportunities. This will be discussed further in another section and plans for future land sharing are ongoing. As noted above, challenges to growing potatoes may have skewed yield results, however this trial was successful and served as a useful bioassay for soils shifting from sheep grazing back into potato production.
While it is hard to determine meaningful changes in soil health over a 2-yr period, there are some interesting observations in this study that warrant more examination. Based on CASH rating system (data not shown), it is clear that the soils overall in this farming area are high quality. However, the soil with the longest history of sheep grazing has the highest organic matter, largest pool of organically bound N (ACE Soil proteins), highest level of metabolic activity of the soil microbial community (Soil Respiration), and best aggregate stability which can be a good indicator of soil biological and physical health (Table 9). Variations in 'active carbon' levels across fields and well as extractable phosphorous and potassium needs further investigation. Sheep grazing following potato production in Wallace 2 also caused some minor improvements in Available Water Capacity, Organic Matter %, and Aggregate Stability, although more information is needed.
Interestingly, Field 4 that did not have a history of sheep grazing and has a rotation history of single species plantings (ie no mixed pasture) had very low beneficial nematode diversity in comparison to the other fields in this study. Observations on beneficial nematode communities over a longer time period and across seasons could be of interest in the future as an indirect measure of soil health and biological diversity. The prevalence of pin nematode (Paratylenchus) across Fields 2-4 as well as the persistence of the root lesion nematode (Pratylenchus) in post-potato production in fields (Wallace 1 & 2) currently in pasture needs to be examined. Pasture plot results indicate that a 2-3 species mix might be sufficient and more cost effective for dairy sheep pasture, especially in comparison to historic pasture results using the standard mix (Table 6 & 7). The influence of pasture species diversity on soil health requires more research.
 Image 1. Existing pasture alongside commercial potato field.
Image 1. Existing pasture alongside commercial potato field.
 Image 2. 2019 Greenhouse Trial set-up.
Image 2. 2019 Greenhouse Trial set-up.
 Image 3. Pre-flowering Greenhouse Trial potato plants
Image 3. Pre-flowering Greenhouse Trial potato plants
 Image 4. 2019 Potato Field Trial
Image 4. 2019 Potato Field Trial
 Image 5. 2020 Potato Field Trial
Image 5. 2020 Potato Field Trial
 Image 6. Rhizoctonia on 'Banana Fingerling' tuber (2019)
Image 6. Rhizoctonia on 'Banana Fingerling' tuber (2019)
 Image 7. Rhizoctonia on 'Chieftan' tuber (2019)
Image 7. Rhizoctonia on 'Chieftan' tuber (2019)
 Image 8. Wire worm damage on'Yukon Gold' tuber (2020)
Image 8. Wire worm damage on'Yukon Gold' tuber (2020)
 Image 10. Curious sheep checking out research plots
Image 10. Curious sheep checking out research plots
 Image 11. Sheep grazing on rented potato ground.
Image 11. Sheep grazing on rented potato ground.
 Image 12. Spring-planted pasture variety trail at 6 months
Image 12. Spring-planted pasture variety trail at 6 months
 Image 13 Fall-planted pasture variety trial after 30 days
Image 13 Fall-planted pasture variety trial after 30 days
 Image 14. Example of tuber size classing (A, B, C)
Image 14. Example of tuber size classing (A, B, C)
Table 1. 2019 Potato Plots
| REP | TYPE | A | B | C | TOTAL | UK | Silver scurf | Rhizoctonia |
| A | Y | 14 | 5.5 | 3.75 | 23.25 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| A | R | 36 | 33.8 | 6.75 | 76.55 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| A | F | 9.2 | 9.2 | 5 | 0 | 1 | ||
| B | Y | 5.7 | 2.9 | 1 | 9.6 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| B | R | 20 | 23 | 4.25 | 47.25 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| B | F | 10.6 | 10.6 | 5 | 0 | 2 | ||
| C | Y | 3.75 | 2 | 0.5 | 6.25 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| C | R | 10.25 | 14.1 | 17.8 | 42.15 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| C | F | 9 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
Tuber weight recorded in lbs./Disease Severity rating scale 0-5 (0=0, 1=0-20%, 2=20-40%, 3=40-60%, 4=60-80%, 5=80-100%)
Table 2. 2020 Potato Plots
| REP | TYPE | A | B | C | TOTAL | UK | Silver scurf | Rhizoctonia | Wire Worm |
| A | Y | 2.75 | 4.25 | 4.5 | 11.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| A | R | 1.75 | 2.5 | 1.75 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A | F | 0 | 1.25 | 3.75 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| B | Y | 3.25 | 3.5 | 7 | 13.75 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| B | R | 1 | 1.25 | 2 | 4.25 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| B | F | 0.25 | 1.75 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C | Y | 2 | 5.25 | 7.5 | 14.75 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| C | R | 5.5 | 3.5 | 4.25 | 13.25 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C | F | 0 | 0.75 | 5 | 5.75 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Tuber weight recorded in lbs./Disease Severity rating scale 0-5 (0=0, 1=0-20%, 2=20-40%, 3=40-60%, 4=60-80%, 5=80-100%)
Table 3. 2019 Greenhouse Field Trial
| REP | TYPE | Weight (oz) | ROT | Silver scurf | Rhizoctonia |
| A | Y | 10 | low | 0 | 0 |
| A | R | 16 | 4 | 0 | |
| A | F | 20 | 0 | 3 | |
| B | Y | 36 | high | 0 | 0 |
| B | R | 23 | 4 | 0 | |
| B | F | 19 | 0 | 2 | |
| C | Y | 9 | 0 | 3 | |
| C | R | 12 | 4 | 0 | |
| C | F | 5 | 4 | 0 |
Table 4. 2019 Pasture Trial Analysis (Collected 9/2019)
| Column1 | Column2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Dry Matter | 22.46 | 17.02 | 22.72 | 16.72 | 13.52 | |
| Crude Protein | 20.11 | 26.05 | 22.4 | 29.15 | 30.49 | |
| Crude Fat | 2.13 | 2.45 | 3.33 | 2.92 | 2.02 | |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 55.74 | 56.53 | 60.51 | 37.87 | 24.87 | |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 27.84 | 22.69 | 32.26 | 23.75 | 21.74 | |
| Lignin | 1.75 | 1.27 | 3.24 | 4.44 | 2.35 | |
| Ash | 9.93 | 12.37 | 12.37 | 11 | 11.24 | |
1-5, pasture species; see pasture type code below
Table 4a. Pasture variety species used for experiment.
| 1 | FESCUE |
| 2 | TIMOTHY |
| 3 | RYE |
| 4 | CLOVER (NZ) |
| 5 | CLOVER (RED) |
Table 5. 2020 Pasture Trial Analysis (Collect 6/2020)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Dry Matter | 25.06 | 25.54 | 27.24 | 16.25 | 16.46 | |
| Crude Protein | 12.25 | 8.68 | 10.42 | 20.58 | 21.91 | |
| Crude Fat | 3.11 | 3.16 | 3.05 | 3.16 | 3.15 | |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 68.63 | 56.01 | 61.28 | 39.54 | 38.43 | |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 35.08 | 32.19 | 36.93 | 31.17 | 29.28 | |
| Lignin | 6.4 | 4 | 6.69 | 6.4 | 6 | |
| Ash | 7.91 | 8.37 | 8.82 | 10.95 | 11.24 | |
1-5, pasture species; see pasture type code below
Table 6. 2019 Existing Pasture-% Dry Matter (Collected 4/2019)
| West | East | |
| Dry Matter | 17.01 | 18.1 |
| Moisture | 82.99 | 81.9 |
| Crude Protein | 3.35 | 2.33 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 4.42 | 4.31 |
| Ash | 1.62 | 1.69 |
| Calcium | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Phosphorous | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Zinc | 3.95 | 336 |
| Manganese | 5.02 | 4.2 |
| Copper | 0.34 | 0.55 |
| Total Dig Nutrients | 10.86 | 11.54 |
| Crude Protein % | 19.72 | 12.89 |
Table 7. 2020 Existing Pasture-% Dry Matter (Collected 6/2020)
| Combined (W & E) | |
| Dry Matter | 25.06 |
| Moisture | 74.94 |
| Crude Protein | 12.25 |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 68.63 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 35.08 |
| Ash | 7.91 |
Table 8. 2020 New Pasture-% Dry Matter (Collected 9/2020)
| Standard Mix |
New Mix |
|
| Dry Matter | 13.28 | 11.6 |
| Moisture | 86.72 | 88.4 |
| Crude Protein | 20.89 | 24.55 |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 49.76 | 43.62 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 34.71 | 31.35 |
| Ash | 9.87 | 10 |
Table 9. 2019-2020 Cornell Assessment of Soil Health
| HF | Wallace 1 | Wallace 2 | Wallace 2* | ||
| AWC | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.28 | |
| Aggregate Stability | 94 | 67.7 | 40.5 | 40.8 | |
| Organic Matter | 6.6 | 5.2 | 4.4 | 4.6 | |
| ACE Soil Protein | 21.2 | 19.3 | 16.9 | 15.5 | |
| Soil Respiration | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| Active Carbon | 748 | 330 | 895 | 807 | |
| pH | 6.4 | 6 | 6.2 | 6.1 | |
| Extractable Phosphorous | 13 | 11.4 | 17.6 | 9.8 | |
| Extractable Potassium | 899.4 | 207.4 | 218.8 | 91.2 | |
*Collected in September 2020, other samples collected May 2019.
Table 10. Nematode Community Analysis
| Plant Parasitic | Bacterial-feeding | Fungal-feeding | |||||||||||
| Field | TOTAL/250 g | Paratylenchus | Pratylenchus | Meloidogyne | Heterodera | Tylenchorychus | Rhabditidae | Cephalobidae | Alaimus | Aphelenchus | Tylenchus | Aphelenchoides | Omnivore |
| 1 | 1540 | 2.6 | 7.8 | 0 | 0 | 9.7 | 22 | 45 | 0 | 4.5 | 5.2 | 0 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 1120 | 39 | 3.4 | 0 | 1.8 | 0 | 5.3 | 34.7 | 6.1 | 0 | 7.7 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 1880 | 42.5 | 1 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 1 | 14.9 | 23.4 | 0 | 2.2 | 5.4 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1389 | 72 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Research outcomes
Education and Outreach
Participation summary:
Preliminary project results were presented at Tilth Alliance Conference (Nov 2020) and the Western Washington Potato Workshop (Feb 2021). Dr. Gigot also participated in a SARE podcast interview (Nov 2019) that aired in 2020. Presentation and farm walk opportunities were limited due to COVID-19 restrictions.
Following, the current global pandemic has significantly delayed the completion of educational and outreach items. However, Dr. Gigot is committed to successfully finishing this work in a timely way within the current year. Dr Kerr will review all publications before they are submitted. While no data has been published yet, the following will be in print or submitted by July 2021:
To Publish:
- A short communication describing the tuber and soil quality findings will be submitted to Agriculture, Ecosystems, and the Environment.
- A feature article for Acres, USA, "Regenerative Relationships: Land Sharing and Soil Health" (query sent March 2021).
- Newsletter/article contributions: Capital Press, Spudman, Dairy Sheep of North America newsletter
Current:
- First blog post 6/25/20: https://harmonyfields.com/farm-journal/sheepandsoilhealth/
- Skagit Valley Herald article: https://www.goskagit.com/news/local_news/skagit-speakers-featured-at-sustainable-ag-conference/article_cea0955d-5040-5811-b101-99a4812f1fad.html
- Animal Welfare Approved: https://agreenerworld.org/west/harmony-fields-bow-wa/
Education and Outreach Outcomes
COVID-19: As a woman-owned farm and a woman-led research project, the global pandemic limited this work. No access to childcare between March 2020-March 2021 made completion of the written deliverables by the original deadlines very challenging. Also, COVID-19 related restrictions prevented farm walks and certain conferences from happening over 2020, which affected outreach.
Other research-related challenges are noted in sections above and research conclusions.