Final Report for GS15-149
Project Information
Screening of essential oils against mycelial growth of L. theobromae showed carvacrol and thymol had effective inhibition on mycelial growth of L. theobromae, with half –inhibition concentrations 0.045 and 0.037 mgmL-1, respectively. Both carvacrol and thymol in shellac coating exhibited effectively activities against diplodia stem end rot (SER) on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit when fruit were artificially inoculated with L. theobromae 12 h before coating application or immediately after coating application. Coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol significantly decreased fruit natural decay, weight loss, and chilling injury during storage, but did not influence fruit internal quality.
Introduction
The grapefruit harvest season can stretch from late September to April or May. Early season grapefruit (September to December) usually reach internal maturity before the peel attains its characteristic external color. Therefore, a commercial degreening treatment that exposes fruit to 5 ppm ethylene at 28 to 29 °C with 90-95% relative humidity (RH) is often necessary because most consumers relate green color with immaturity (Ritenour et al., 2003a). However, the degreening environment can significantly increase diplodia stem-end rot (SER), caused by Lasiodiplodia theobromae, on citrus fruit (Brown, 1986; Zhang, 2004).
Diplodia SER is often the most important postharvest disease of citrus fruit in warm and humid regions such as Florida. Spores of L. theobromae infect immature citrus fruit on the tree and then remain quiescent in the necrotic floral tissue (Brown, 1971). After fruit maturity, L. theobromae can be isolated from most citrus fruit in Florida. At or after harvest, hyphae grow through the developing abscission zone and into the peel, flesh, and central core of the fruit. Growth of L. theobromae is maximum at 30 °C, and RH at 95-100% can promote conidia germination (Barmore and Brown, 1985). During degreening, high temperature and RH conditions promote fungal growth on fruit, while ethylene speeds the formation of the abscission zone, reduces natural resistance of fruit tissue to pathogen, and promotes hyphal penetration into the flesh (Barmore and Brown, 1985; Brown and Burns, 1998). Without adequate control measures, diplodia SER can develop rapidly during degreening and subsequent transport to become serious problems upon arrival at destination markets.
In Florida, thiabendazole (TBZ), imazalil (IMZ), and sodium-o-phenylphenate (SOPP) are commonly used to control postharvest decay on fresh citrus. However, all three have been used for more than three decades and their intense and repeated use can result in pathogen resistance to the fungicides, which has developed in many other regions of the world (Mari et al., 2014). In addition, consumer desires for reduced pesticide use and lower residues in general are encouraging investigations into more natural products (Zhang and Swingle, 2005). Furthermore, fungicide residues can limit citrus export because of lower maximum residue limits (MRLs) in many importing countries compared to the United States. For example, IMZ grapefruit MRLs are 10 ppm in the US, but only 5 ppm in Europe, Canada, and Japan. TBZ and SOPP grapefruit MRLs are 10 ppm in the US, but only 5 ppm in Europe. Therefore, effective and safe alternative methods to control postharvest decay of citrus are needed.
In recent years, more attention has focused on exploitation of natural plant products that have little impact on human health or the environment to control postharvest disease. Essential oils are aromatic, oily liquids extracted from plant organs that are recognized as safe for human health and the environment (Antunes and Cavaco, 2010). Therefore, research into their use has expanded. Because of their antifungal activity, many essential oils have been reported to control postharvest disease caused by Penicillium spp., Alternaria spp., Botrytis cinerea, or Monilinia fructicola on a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables (Antunes and Cavaco, 2010). Jhalegar et al. (2015) found that dipping mandarin fruit in lemon grass oil, clove oil, eucalyptus, and neem oil significantly inhibited green (P. italicum) and blue (P. digitatum) mold. du Plooy et al. (2009) also reported that Mentha spicata and Lippia scaberrima essential oils, as well as pure limonene and carvone incorporated in wax coating showed significant effects against blue and green mold on oranges. Usually, the composition, structure, and functional group of essential oils play an important role in their antifungal activity, and compounds with phenolic groups are most effective (Dorman and Deans, 2000). Both carvacrol and thymol are phenolic compounds and have been reported to have antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea, Monilinia fructicola, Rhizopus stolonifer, Alternaria arborescens, Geotrichum candidum, Colletotrichum acutatum, Botryodiplodia theobromae, Phytophthora cactorum, and Cryponectria parasitica (Kim et al, 2008; Numpaque et al., 2011; Plotto et al., 2002; Tsao and Zhou, 2000).
Unfortunately, there can be drawbacks to applying essential oils on fresh fruit for postharvest decay control, such as the development of peel injury. Amiri et al. (2008) reported that dipping fruit in an aqueous 1 mgmL-1 eugenol solution resulted in peel injury on apple. Yan et al. (2016) also found that dipping fruit in an aqueous 2 mgmL-1 carvacrol or thymol solution resulted in phytotoxic peel injury on ‘Valencia’ oranges, but no injury developed when the same or even greater concentrations were incorporated into the wax coating. It was also reported that wax coating immediately after heat treatment greatly reduced the development of visible heat injury on ‘Marsh’ grapefruit. These coatings can slow fruit water loss and restrict oxygen diffusion to inhibit oxidative peel browning and symptom development (Ritenour et al., 2003b). Another advantage of incorporating essential oils into wax coatings is that essential oils are likely released slowly onto the product surface to better maintain their concentration during storage. In dipping treatment, the protective activity provided by essential oils decreases right after treatment because of their volatility. Kouassi et al. (2012) found that the effective concentration of Cinnamomum zeylanicum essential oil allowing 100% disease control was reduced to 0.5% after incorporating into shellac wax, while an effective concentration of C. zeylanicum essential oil into ethanol was 5% (Kouassi et al. 2010). In addition, coating citrus fruit with carnauba or shellac is an important process in Florida commercial packinghouse to reduce subsequent water loss and improve gloss, which also makes incorporating essential oils into wax practicable for commercial application.
The objectives of this study were, 1) to evaluate the efficacy of carvacrol and thymol against Lasiodiplodia theobromae in vitro; and 2) to evaluate the ability of carvacrol and thymol, incorporated into a commercial shellac coating, to control diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
Literature Cited:
Amiri, A., R. Dugas, A.L. Pichot and G. Bompeix. 2008. In vitro and in vitro activity of eugenol oil (Eugenia caryophylata) against four important postharvest apple pathogens. Int. J. Food Microsc. 126(1): 13-19.
Antunes, M.D.C. and A.M. Cavaco. 2010. The use of essential oils for postharvest decay control. A review. Flavor Frag. J. 25: 351-366.
Barmore, C.R. and G.E. Brown. 1985. Influence of ethylene on increased susceptibility of oranges to Diplodia natalensis. Plant Dis. 69: 228-230.
Brown, G.E. 1971. Pycnidial release and survival of Diplodia natalensis spores. Phytopathology. 61:559-561.
Brown, G.E. 1986. Diplodia stem-end rot, a decay of citrus fruit increased by ethylene degreening treatment and its control. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 99: 105-108.
Brown, G.E. and J.K. Burns. 1998. Enhanced activity of abscission enzymes predisposes oranges to invasion by Diplodia natalensis during ethylene degreening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 14: 217-227.
Dorman, H.J.D. and S.G. Deans. 2000. Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88: 308-316.
du Plooy, W., T. Regnier and S. Combrinck. 2009. Essential oil amended coatings as alternatives to synthetic fungicides in citrus postharvest management. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 53: 117-122.
Jhalegar, M.J., R.R. Sharma and D. Singh. 2015. In vitro and in vivo activity of essential oils against major postharvest pathogens of Kinnow (Citrus nobilis× C. deliciosa) mandarin. J. Food Sci. Tech. 52(4): 2229-2237.
Kim, J., Y.S. Lee, S.G. Lee, S.C. Shin and I.K. Park. 2008. Fumigant antifungal activity of plant essential oils and components from West Indian bay (Pimenta racemosa) and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) oils against two phytopathogenic fungi. Flavor Frag. J. 23(4): 272-277.
Kouassi, K.H.S., M. Bajji and H. Jijakli. 2012. The control of postharvest blue and green molds of citrus in relation with essential oil-wax formulations, adherence and viscosity. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 73: 122-128.
Kouassi, K.H.S., M. Bajji, A. Zhiri, P. Lepoivre and M.H. Jijakli. 2010. Evaluation of three essential oils as potential sources of botanical fungicides. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 75(4): 525-529.
Mari, M., A.D. Francesco and P. Bertolini. 2014. Control of fruit postharvest disease: old issue and innovative approaches. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 1:1-4.
Numpaque, M.A., L.A. Oviedo, J.H. Gil, C.M. García and D.L. Durango. 2011. Thymol and carvacrol: biotransformation and antifungal activity against the plant pathogenic fungi Colletotrichum acutatum and Botryodiplodia theobromae. Trop. Plant Pathol. 36 (1):3-13.
Plotto, A., D.D. Roberts and R.G. Roberts. 2002 Evaluation of plant essential oils as natural postharvest disease control of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). In XXVI International Horticultural Congress: Iss. Adv. in Postharvest Hort. 628: 737-745.
Ritenour, A.M., M.M. William and W.W. Wardowski. 2003a. Recommendations for degreening Florida fresh citrus fruits. Florida Cooper. Ext. Serv. 1170: 1-3.
Ritenour, M.A., K.J.J. Karuppiah, R.R. Pelosi, M.S. Burton, T.G. Mccollum, J.K. Brecht and E.A. Baldwin. 2003b. Response of Florida grapefruit to short-duration heat treatments using vapor heat or hot water dips. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 116: 405-409.
Tsao, R. and T. Zhou. 2000. Antifungal activity of monoterpenoids against postharvest pathogens Botrytis cinerea and Monilinia fructicola. J. Essent. Oil Res. 12(1): 113-121.
Zhang, J. 2004. Effect of ethylene on natural resistance of citrus fruit to stem-end rot caused by Diplodia natalensis and its relation to postharvest control of this decay. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 117: 364-367.
Zhang, J. and P.P. Swingle. 2005. Effects of curing on green mold and stem-end rot of citrus fruit and its potential application under Florida packing system. Plant Dis. 89(8): 834-840.
The over goal of this project is to evaluate the efficiency of natural compounds in ambient and heated solutions to control stem-end rot (SER), caused by L. theobromae, on grapefruit during postharvest handling and marketing.
Objective 1. Screen essential oil compounds for their efficacy against L. theobromae in vitro. Study the effects of promising compounds to inhibit mycelium growth and conidial germination of L. theobromae.
Objective 2. Using the most effective essential oil compounds from objective 1, evaluate their ability in both ambient and heated solutions to control SER on inoculated grapefruit and on naturally infected fruit.
Objective 3. Test the effects of essential oil compounds in ambient or heated solutions on fruit internal and external quality during postharvest handling and simulated marketing conditions.
Research
Objective 1. Screen essential oils for their efficacy against L. theobromae in vitro. Study the effects of promising compounds to inhibit mycelial growth of L. theobromae.
- Screening of essential oils against mycelial growth of L. theobromae
Benzaldehyde, carvacrol, citral, cinnamaldehyde, ethanol, eugenol, eucalyptol, menthol, trans-cinnamaldehyde, and thymol were evaluated against mycelial growth of L. theobromae isolated from infected ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit in vitro.
- Studying the effects of carvacrol and thymol to inhibit mycelial growth of L. theobromae
Carvacrol and thymol were amended in PDA medium at difference concentrations (0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.5 mg/mL) to test their antifungal activities against mycelial growth of L. theobromae.
Objective 2. Using the most effective essential oils from Objective 1, evaluate their ability in a commercial shellac coating to control diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
- Finding out the optimal diplodia SER inoculation method
In this study, ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit were randomly separated into three groups, surface sterilized with 75% (v/v) ethanol, and wounded with a sterilized nail at the fruit blossom, equator, or stem area (3 mm deep by 3 mm wide), respectively. Mycelial plug was placed on each wound site. And then, fruit were incubated either at 29 °C, or at room temperature (23 °C), both at 90% RH and in darkness.
- Evaluate carvacrol and thymol in a commercial shellac coating to control diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
Preliminary experiment showed that both carvacrol and thymol at low concentration (0.2%) in water resulted in phytotoxic peel injury on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit, while no injury was detected when coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol, even at high concentration (1.0%). Considering the commercial application practicality, we changed essential oil dipping treatment to essential oil coating treatment.
In this study, carvacrol and thymol were mixed in a commercial shellac wax (590 HS) to determine their activities against diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit. Fruit were artificially inoculated with L. theobromae 12 h before coating application or immediately after coating application and incubated at 29 °C with 90% RH for 48 h.
Objective 3. Test the effects of essential oils in a commercial shellac coating on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit quality during postharvest handling and simulated marketing conditions.
Fruit were coated with shellac containing 1.0% carvacrol or thymol on packingline and stored at 10 °C with 90% RH for 8 weeks followed by 1 week at 25 °C with 60% RH. Fruit qualities were evaluated 4 and 8 weeks after cold storage, and 1 week after room temperature storage. For chilling injury evaluation, fruit were stored at 5 °C with 90% RH for 8 weeks followed by 1 week at 25 °C and 60% RH.
Objective 1. Screen essential oils for their efficacy against L. theobromae in vitro. Study the effects of promising compounds to inhibit mycelial growth of L. theobromae.
- Screening of essential oils against mycelial growth of L. theobromae
Exposure to benzaldehyde, citral, cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, eucalyptol, and trans-cinnamaldehyde volatiles (50 μL/L) did not inhibit mycelial growth. However, carvacrol volatile at 50 μL/L effectively inhibited mycelial growth, with the percent inhibition 98% (Figure 1-A). In amended PDA medium, carvacrol and thymol at 0.1 mg/mL inhibited mycelial growth by 93% and 97%, respectively, while ethanol and menthol had no antifungal activity against L. theobromae (Figure 1-B).
- Studying the effects of carvacrol and thymol to inhibit mycelial growth of L. theobromae
In amended PDA medium, carvacrol and thymol inhibited mycelial growth in a concentration-dependent manner, with higher concentration having a higher efficiency. Half-inhibition concentration of carvacrol and thymol against mycelial growth was 0.045 and 0.037 mg/mL, respectively (Figure 2).
Objective 2. Using the most effective essential oils from Objective 1, evaluate their ability in a commercial shellac coating to control diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
- Finding out the optimal diplodia SER inoculation method
Result showed that fruit inoculated at blossom with mycelial plug and incubated at 29 °C with 90% RH developed 100% infection with uniform lesion area after 48 h incubation (Figure 3 A). When mycelial plugs were removed 12 h after inoculation, fruit also developed 100% infection 48 h after inoculation (Figure 3 B). That indicates that L. theobromae can invade fruit fresh within 12 h under the current inoculation condition, although lesions did not show up until 48 h after inoculation.
- Evaluate carvacrol and thymol in a commercial shellac coating to control diplodia SER on artificially inoculated ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
When fruit were inoculated before treatment, shellac containing 1.0% carvacrol or thymol inhibited lesion development by 59% or 37%, respectively, compared to shellac alone after 48 h incubation (Figure 4). When fruit were inoculated immediately after treatment, fruit coated with shellac containing 1.0% carvacrol or thymol exhibited only 5% or 25% disease incidence, respectively after 24 h incubation, while 92% of the control fruit exhibited diplodia SER lesions (Figure 5 A and B). After 48 h incubation, coating fruit with shellac containing 0.1% carvacrol or thymol inhibited lesion development by 43% or 24%, respectively, compared to shellac alone (Figure 5 C and D).
Objective 3. Test the effects of essential oils in a commercial shellac coating on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit quality during postharvest handling and simulated marketing conditions.
After 8 weeks storage, only 17% or 14% of fruit showed natural decay when they were coated with shellac containing 1.0% carvacrol or thymol, respectively, while 23% of the control fruit and 31% of shellac alone-coated fruit developed natural decay (Figure 6). Coating fruit with shellac alone significantly inhibited fruit weight loss by 20% after 8 weeks storage. Carvacrol and thymol in shellac coating significantly enhanced the efficiency of shellac coating on fruit weight loss reduction, 18% and 13%, respectively (Figure 7). After 8 weeks storage at 5 °C and 90%, most control fruit developed chilling injury, and the chilling injury became severer when fruit were transferred to room temperature (25 °C and 60% RH) for 1 week. After 8 weeks cold storage followed by 1 week room temperature, coating fruit with shellac alone reduced chilling injury by 28%, while the addition of carvacrol or thymol in shellac coating significantly reduced chilling injury by 73% or 70%, respectively, compared to control fruit (Figure 8). None of treatments significantly influenced fruit total soluble solids (TSS), titratable acid (TA) and the ratio TSS:TA of ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit (Table 1)
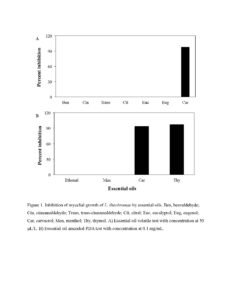 Figure 1. Inhibition of mycelial growth of L. theobromae by essential oils. Ben, benzaldehyde; Cin, cinnamaldehyde; Trans, trans-cinnamaldehyde; Cit, citral; Euc, eucalyptol; Eug, eugenol; Car, carvacrol; Men, menthol; Thy, thymol. A) Essential oil volatile test with concentration at 50 μL/L. B) Essential oil amended PDA test with concentration at 0.1 mg/mL.
Figure 1. Inhibition of mycelial growth of L. theobromae by essential oils. Ben, benzaldehyde; Cin, cinnamaldehyde; Trans, trans-cinnamaldehyde; Cit, citral; Euc, eucalyptol; Eug, eugenol; Car, carvacrol; Men, menthol; Thy, thymol. A) Essential oil volatile test with concentration at 50 μL/L. B) Essential oil amended PDA test with concentration at 0.1 mg/mL.

Figure 2. Inhibition of mycelial growth of L. theobromae by different concentrations of carvacrol (A) or thymol (B). 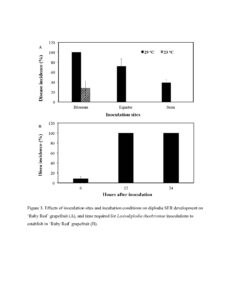
Figure 3. Effects of inoculation sites and incubation conditions on diplodia SER development on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit (A), and time required for Lasiodiplodia theobromae inoculations to establish in ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit (B).
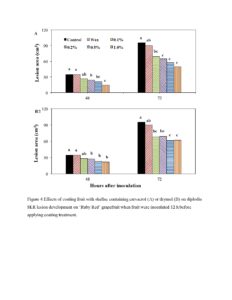
Figure 4 Effects of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol (A) or thymol (B) on diplodia SER lesion development on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit when fruit were inoculated 12 h before applying coating treatment. 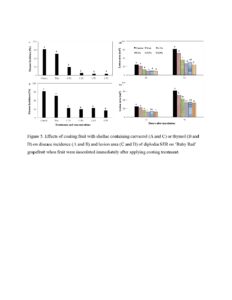
Figure 5. Effects of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol (A and C) or thymol (B and D) on disease incidence (A and B) and lesion area (C and D) of diplodia SER on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit when fruit were inoculated immediately after applying coating treatment.
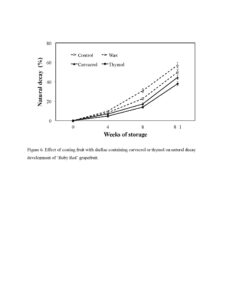
Figure 6. Effect of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol on natural decay development of ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
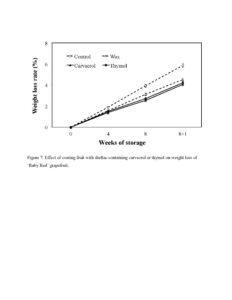
Figure 7. Effect of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol on weight loss of ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit. 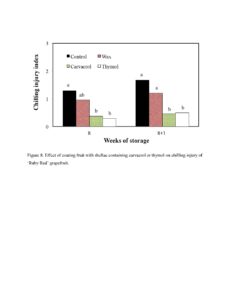
Figure 8. Effect of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol on chilling injury of ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit.
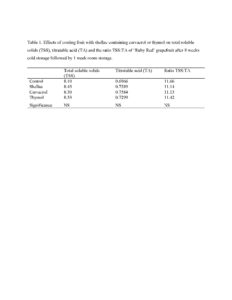
Table 1. Effects of coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol on total soluble solids (TSS), titratable acid (TA) and the ratio TSS:TA of ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit after 8 weeks cold storage followed by 1 week room storage.
Educational & Outreach Activities
Participation Summary:
Abstracts/Presentations:
Yang, J., C. Hu, J. Li, and M.A. Ritenour. 2016. Use of Carvacrol and Thymol to Inhibit Growth of Lasiodiplodia Theobromae in Vitro and Control Stem-End Rot on ‘Ruby Red’ Grapefruit. FSHS 2016 Program and Abstracts; available at http://www.fshs.org/
Publications:
Yan g, J., J. Li, C. Hu, L Deng, and M.A. Ritenour. 2016. Use of carvacrol and thymol to inhibit growth of Lasiodiplodia theobromae in vitro and control stem-end rot on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit. HortScience (submitted)
Project Outcomes
The current study identified an effective method to control postharvest Diplodia SER on ‘Ruby Red’ grapefruit instead of fungicide treatment. Coating fruit with shellac containing carvacrol or thymol showed effectively activity against diplodia SER on grapefruit inoculated with L. theobromae. Essential oils are aromatic oily liquids extracted from plant organs that are recognized as safe for human health and the environment. The US Food and Drug Administration has listed some essential oils as food for human consumption. Our finding from this this study could provide a safe and effective strategy to control diplodia SER in fresh citrus from Florida.
Economic Analysis
There are currently no known economic returns from this project. However, in the near future, outcomes from this project could prevent tremendous economic losses in the industry. In particular, the past year has seen a large increase in the number of reports of diplodia stem-end rot at export destination markets. So much so, that the Florida Citrus Packers Association met with the PI (Dr. Mark Ritenour) and USDA researchers about developing a systems approach to reduce the incidence of this disease, especially in fruit destined for Japan where the occurrence of this disease causes “mandatory segregation,” which means the fruit must be repacked after arrival at substantial cost to the shipper to assure all diseased fruit are removed before further marketing. Using fresh grapefruit exported to Japan as an example, the fruit may sell for between $15 to $20 per carton (4/5 bu) and a single load (shipping container) of fruit holds approximately 1,260 cartons. Therefore, each load of grapefruit is worth $18,900 to $25,200. Complete losses are rare, but do occur occasionally when, for example, pesticide residues exceed allowable limits. However, it is not uncommon for fruit failing to meet quality standards to reduce returns by perhaps 25%. If 10% of the loads develop diplodia stem-end rot, losses could equal perhaps $5 million per season.
Farmer Adoption
There is no adoption of the technology at this time into commercial packinghouses because further studies are needed to refine the technology (see below). However, it is anticipated that perhaps only another year of study might be needed before the technology is ready for commercial application.
Areas needing additional study
The use of the identified essential oils is promising, but more work is needed before commercial application. Specifically, because there are different waxes used for fresh citrus (e.g., shellac and carnauba, and those containing morpholine or ammonia), work is needed to evaluate solubility and efficacy after incorporation into these different media. For example, formulations may need to be adjusted to allow better solubility. In addition, even if packers do not completely switch from traditional fungicides to the use of these essential oils, they may want to added the essential oils in addition to the fungicides to potential reduce fungicide concentrations or to enhance decay control beyond what they achieve now. Compatibility of such mixtures in aqueous and wax solutions needs to be evaluated first.